EDIP
The main purpose of this model is to be able to estimate the impact that transport policy choices have on equity and income distribution as well as their energy and environmental effects. EDIP models the production and consumption activities of 59 sectors and related products. Each sector has its emissions, which are coupled partially to the production activities and partially to the energy use. The labour market has been strongly developed, where wages differ by level of education, profession, and sector. This is linked to the welfare of five income quintiles. The transport sector in the model has been developed in detail, with TREMOVE data incorporated in the model for complex analysis of transport problems. The current base year for the datasets is 2009, which is the year of the latest available input-output tables from EUROSTAT. The EDIP models are useful for simulating transport and environment policy, but differ from other models in the sense that they add visibility on the social dimension of the policy.
The model covers the EU 27 countries plus Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, and Croatia, with the following characteristics (one model per country):
- Different household types with CES use function:
- Five income classes.
- Three population density classes.
- Six family types.
- 59 commodities, used in production and consumption.
- 31 factors of production: capital, labour, and goods.
- Detailed modelling of transport use by firms and households:
- Two distance classes.
- Three transport modes.
- Own production of road transport (sustainable/non-sustainable).
Recente projecten

Impact of the Belgian Truck Kilometre Charge on the Food Industry
What are the direct costs and economic impact of truck kilometre charge on the food industry?

Evaluation of CO2-regulation measures for light freight vehicles beyond 2020
TML shed light on possible design options for CO2 regulations for cars and light freight vehicles.

e-Freight
We optimised the efficiency of information exchange for multimodal freight transport.

Cost Benefit Analysis Corridor PP22
How can the European rail corridor between Germany and Greece be finished and what are the consequences?

ToPDAd
We developed innovative socio-economic methods and models to enable impact analysis of regional adaptation policies.

Update of elasticities in the HERMIN model
We identified and aggregated the elasticities of spillover effects through input-output linkages and externalities in the mai...
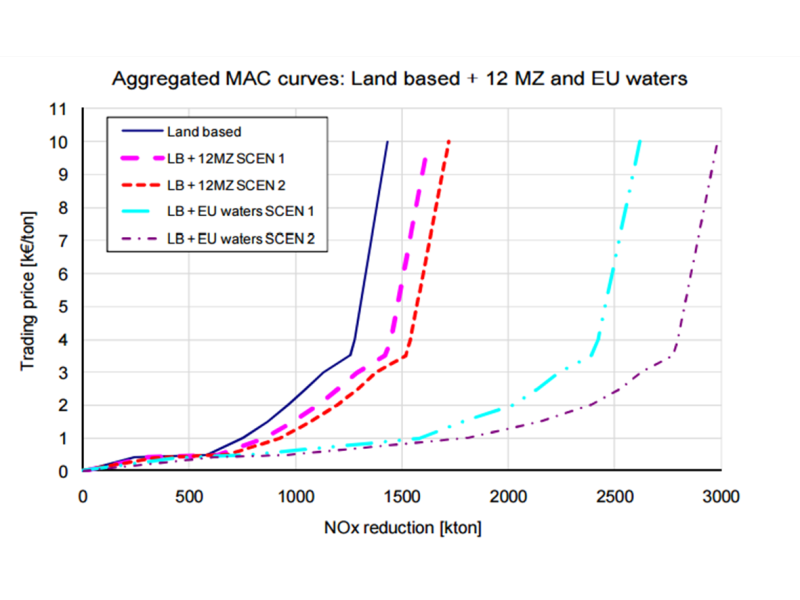
Market-based instruments for reducing air pollution
We evaluated policy options for reducing air pollution from maritime shipping.

REFIT
We improved and tested sustainability indicators and models with respect to European transport policy choices.

